Compression is a fundamental tool used to manage the dynamic range of audio, ensuring consistency and balance in a mix. It plays a crucial role in both the mixing and mastering stages, shaping the sound and feel of a recording.
How Does Audio Compression Work?
Audio compression reduces the dynamic range of a recording - the difference between the loudest and quietest parts. It makes the quieter sounds more audible and prevents the louder ones from becoming overwhelming. Here's a breakdown of how compression works and its key controls:
- Threshold. This is the level at which compression starts to occur. Sounds above the threshold are compressed, while those below remain unaffected.
- Ratio. This determines how much compression is applied. A 4:1 ratio means that for every 4 dB above the threshold, the output is reduced to 1 dB.
- Attack. The attack time sets how quickly the compressor reacts to sounds exceeding the threshold. A faster attack time results in immediate compression, which is useful for taming sharp transients.
- Release. Opposite to attack, release time determines how quickly the compression stops after the sound falls below the threshold. Longer release times can smooth out a track.
- Knee. The knee controls how the compressor transitions from non-compression to compression around the threshold. A 'hard' knee is abrupt, while a 'soft' knee is more gradual.
- Make-up gain. After compression reduces the overall level, make-up gain brings the level back up to a desired volume.
What is Compression Used For?
In music production, compression serves several purposes:
- Balancing levels. It evens out inconsistencies in vocal or instrument performances, leading to a more uniform sound.
- Controlling transients. Sharp sounds like drum hits can be tamed for a smoother sound.
- Adding punch. Strategic compression can add energy and 'punch' to drums or bass.
- Enhancing clarity. It can bring out nuances in a mix, making individual elements more distinct.
- Dynamic control in mixing and mastering. During mixing, it helps blend tracks together. In mastering, it ensures the overall sound is cohesive and polished.
Compression Tools
Most Digital Audio Workstations (DAWs) come with built-in compression tools. For instance, Logic Pro offers the Compressor plugin, while Ableton Live includes the Glue Compressor and Dynamics.
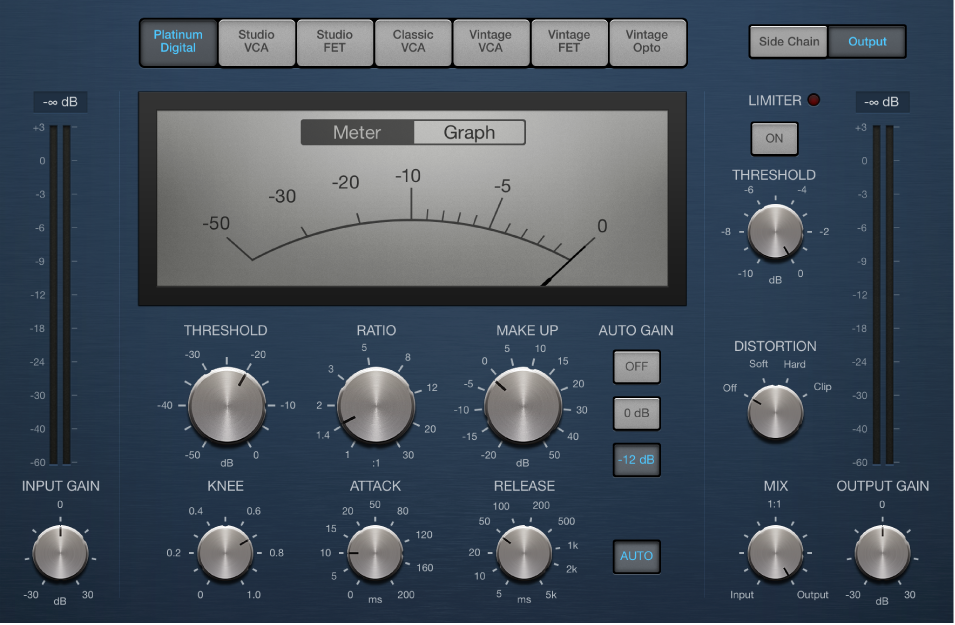
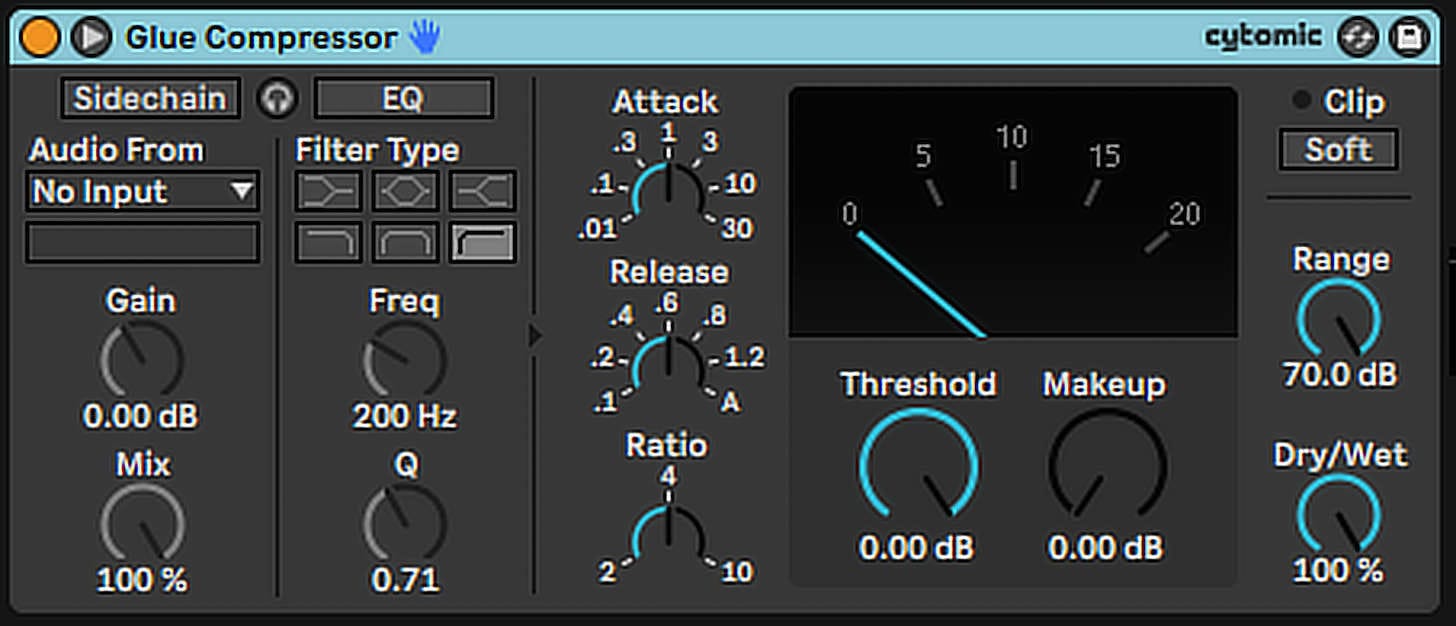
Besides these, numerous third-party plugins, like the Waves C1 Compressor or the FabFilter Pro-C2, offer additional features and sonic characteristics.
Choosing a compression tool boils down to personal preference and availability within your DAW.
FAQs
What's the difference between compression and limiting?
Limiting is a form of extreme compression with a very high ratio, primarily used to prevent clipping and overly loud signals.
How do I avoid over-compressing?
Listen critically and compress in stages. Too much compression can make a mix sound lifeless or 'squashed'.
Can compression fix all dynamic issues in a mix?
While it helps, it's not a cure-all. Proper recording techniques and gain staging are also crucial.
What's side-chain compression?
This is when an external source triggers the compressor. It's often used in dance music, where the bass is compressed in response to the kick drum.
Do different genres require different compression approaches?
Yes. For example, jazz might require subtle compression to retain dynamics, while pop music often uses more aggressive compression for a consistent sound.
What happens if I don't use compression in my music?
Without compression, some parts of your music might be too quiet to hear, while others could be too loud and overpowering. Compression helps maintain a consistent volume, making your music sound more professional and enjoyable.
Can I use compression in a live performance?
In a live setting, compression can help control the dynamics of vocals and instruments. Start with moderate settings and adjust based on the venue and the performance. Keep in mind that live compression is about enhancing the sound in real-time, so practice and listen to how it affects the overall mix.